The SaaS market has doubled since 2014 — growing to $157 billion in value by 2020. This means that the software industry is increasingly competitive, so optimizing your SaaS sales process is key to ensuring business growth.
Based on our 15+ years of experience, our sales experts have perfected a proven B2B SaaS sales process that can help build your sales pipeline with relevant leads and close more deals.
We’ll discuss:
- What is B2B SaaS sales?
- Our proven B2B software sales process
- The factors that can impact your sales process
Let’s first brush up on the B2B SaaS sales basics.
What is B2B SaaS Sales?
B2B SaaS sales is the process of selling cloud-based software-as-a-service that helps clients grow their organizations and achieve their business goals. A few examples of these software products include Salesforce Sales Cloud, Google Workspace, and Adobe Creative Suite.
There are many different types of SaaS products out in the market today, but they can all generally fit within one of two software sales models based on who their customers are.
What are the B2B SaaS selling models?
The 2 different types of B2B SaaS sales models are transactional sales and enterprise sales.
Transactional sales work better for high-volume sales with shorter sales cycle and faster onboarding time. These companies usually require support operations that can quickly handle customer inquiries quickly and effectively. They tend to rely on marketing to attract inbound leads so they can focus their resources on providing quality customer service to their existing customers.
Enterprise sales work for organizations with low-volume sales, longer sales cycles, and a higher average selling price (ASP). Because their customers tend to take a longer time to make a final decision, many companies use sales development reps (SDRs) to focus on introducing as many high-quality prospects into the sales funnel as possible. If you’re looking for information about how to get your foot in the door with enterprise customers, be sure to visit our post “How to Sell Your Software to a Big Company.”
Each industry has its own challenges, so the software world is no different. Let’s jump into what makes the B2B SaaS world so different.
Unique B2B SaaS challenges in sales
The biggest difference between B2B SaaS sales and B2C SaaS sales is that you’re trying to win over more decision makers when selling to businesses — thus prolonging your sales cycle.
There are many other barriers our software clients face on a daily basis, such as:
- Complex product with customization options
- Utilizing unique SaaS sales tactics (such as free trials and freemium tiers)
- Complex selling and compliance restrictions
- Reliance on customer retention
Now that you have a clearer understanding of the challenges your sales team may face, it’s time to explore our proven B2B SaaS sales process. This process works especially well for enterprise sales.
B2B software sales process
This SaaS sales process has been refined by our sales experts to help you maximize your sales pipeline while minimizing your sales cycle. Following the infographic below, we’ll walk you through each step in detail.
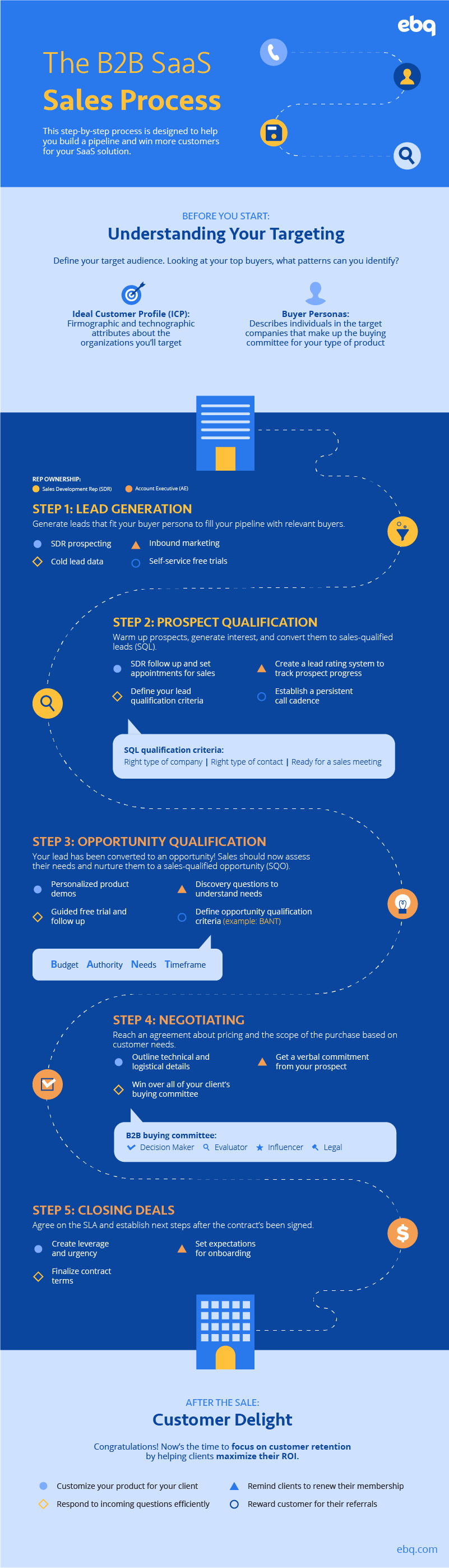
Before the sales process:
Understanding your target
Take this time to define both your ideal customer profile (ICP) and buyer personas. What type of companies and which job titles within those companies should you target? Looking at your top buyers, what patterns can you identify? This will help your sales team find and prioritize who to target based on which contact fits your profile and personas.
We also recommend identifying which B2B SaaS sales model to implement at this stage: the transactional sales model or the enterprise sales model. By figuring out which model works best for your organization and your buyers, you’ll be able to figure out how to allocate your resources.
Step 1:
Lead generation
This is when you focus on generating as many leads as possible that fit your buyer personas and ICPs. Because your goal is to fill up your prospect database, you should consider hiring a data vendor to support your prospecting needs. Be sure to exercise caution when choosing where your data comes from, as not all B2B contact databases are created the same.
You’ll also need to rely on both inbound and outbound leads during this step. For inbound leads, you should take the time to strengthen your marketing efforts and campaigns to establish trust between your prospects and your organization. These marketing efforts can be anything from an online advertisement to a web chat; we’ve covered a few more examples in our post, “Marketing-Qualified Lead Sources and Their Impact On Your Pipeline.”
When pursuing outbound leads, your SDRs will need to make the first contact with prospects. SDRs are in charge of reaching out to cold leads and following up on marketing leads. Their primary goal is to set appointments for sales reps, so an SDR is able to dedicate the time and effort required for prospecting.
Another way to generate SaaS leads is with self-service free trials, which can be offered to help prove your solution’s value to your customers at less risk to them. Your SDR team should follow up with these prospects to make sure they are maximizing their free trials by addressing any concerns and roadblocks immediately. For more tips on SaaS free trials, be sure to visit our “SaaS Free Trial Best Practices to Improve Conversions” post.

Interested in the Best Cold Calling Scripts for Software Sales?
Our guide includes sales expert’s insights and best practices. Free for anyone who’s ready to create high-converting scripts.
Step 2:
Prospect qualification
As leads begin to trickle into your sales pipeline, your SDRs should be following up with prospects on a regular basis using a strategic and persistent call cadence. The SDR’s goal is to qualify leads and warm them up until they’re ready to speak to a sales rep.
Be sure to set clear lead qualification criteria to evaluate who is a sales-qualified lead (SQL). Lead qualification criteria are characteristics that indicate whether a prospect is a good fit to become a customer. Once you find the right person to talk to within the right type of company, who agrees to a sales meeting, the SDR can convert them to an SQL.
Because you don’t want any prospects to slip past your SDRs, you’ll need to hire an experienced sales development team who understands how to follow up with prospects effectively. For example, EBQ’s SDRs are trained to call on both cold and inbound leads and qualify them against a variety of unique criteria. Visit our outsourced sales development page to learn more.
After your prospect passes through this step, your SDR should pass this prospect to the account executive for further nurturing. To help make the handoff smoother, your SDRs should manage calendar invites and join the meeting to introduce the sales rep.
Step 3:
Opportunity qualification
At this point, your prospect can be considered an opportunity. However, the work doesn’t stop there. Your sales rep should continue nurturing these opportunities — such as by conducting customized product demos, asking further discovery questions, and learning more about your opportunity’s needs.
You should further qualify these prospects as a sales-qualified opportunity (SQO) by using an opportunity qualification process, which validates if a prospect is likely to purchase. One of the most popular qualification techniques is the BANT framework, which focuses on the prospect’s budget, authority, needs, and timeline to analyze if the opportunity is the right fit.
Remember: Your sales reps should be consistently qualifying throughout the entire sales process. Just because a prospect says they’re going to purchase doesn’t mean they’ll actually convert in the end. You need to make sure there’s continuous momentum before you move your prospect to the next step. We want to reiterate that this momentum should be built on prospect activities — such as involving other stakeholders or asking for contract details.
If you’re tracking opportunities in your CRM, you can forecast the probability of a deal going through by assigning percentages to different sales stages. For example, during the opportunity qualification step, our sales experts recommend moving these prospects to a “qualified” stage in your CRM with a forecasted 25% chance of conversion. Read more about forecasting using CRM pipeline stages in our post about understanding the sales cycle.
Step 4:
Negotiating
The goal in the negotiation step is to reach an agreement that satisfies both your client and your organization.
As the decision makers determine if your solution is a right fit for their business, your AEs need to be able to answer all of their questions — both technical and logistical. Your goal is to remove any final roadblocks that may be preventing your prospects from converting.
At this point, your AEs should be working with all of your customer’s stakeholders, such as their full buying committee and legal team, to help prevent those last-minute roadblocks. The AE can also work with your internal stakeholders (such as your customer service team) to prepare for onboarding the customer. That way, you can work to finalize contract details to persuade the prospect to convert.
At this step of the sales process, our sales experts recommend you move these prospects under the “negotiation” stage in your CRM with a 50% probability of converting. Remember these probability recommendations are a starting point for your CRM sales process, but you should continually assess the accuracy of your forecasting as you collect more data.
Step 5:
Closing deals
Your goal is to make the sale, so make sure to create leverage and urgency to convince your prospect to convert. This is when your prospect needs to agree on your terms before anything is signed. If you’re looking for ways to close the sale, be sure to read our “How to Close The Deal with B2B Sales Closing Techniques” post.
Once you hear a verbal commitment from your prospect, you can predict a 75% probability of closing; these prospects should be moved to the penultimate “commit” stage in your CRM.
After the deal has been finalized, your AE will need to set expectations on the next steps. From there, you can label these prospects in the “closed won” stage.
Because your sales team is key to generating revenue and ensuring business growth, it’s important to hire experienced AEs who can effectively follow through with each prospect to close the sale. Many organizations choose to outsource their sales team to benefit from the vendor’s experience. In fact, our clients are drawn to our outsourced sales team because of our proven sales strategies across multiple industries.
After the sales process:
Customer delight
Congratulations on converting your prospects into customers! Now, it’s time to prove your value and help your customers maximize their ROI.
To do so, your onboarding team needs to help prove your solution’s value within the first 30 days of implementation. This may include anything from educating them on how to customize the tool for their needs to even connecting their existing tools with your SaaS.
From there, your customer service team needs to be responsive to any of their needs; this is the best way to prove your value. We’ve also outlined how to increase sales revenue with customer service in another post.
Finally, you should remind them to renew their subscriptions and even reward your customers for their referrals. The respective account managers should be the ones handling renewals and looking for cross-selling and upselling opportunities.
Key B2B SaaS sales metrics
You’ll need to track and measure a few SaaS sales metrics to gauge your sales team’s level of success. Here are a few metrics that our sales leaders track:
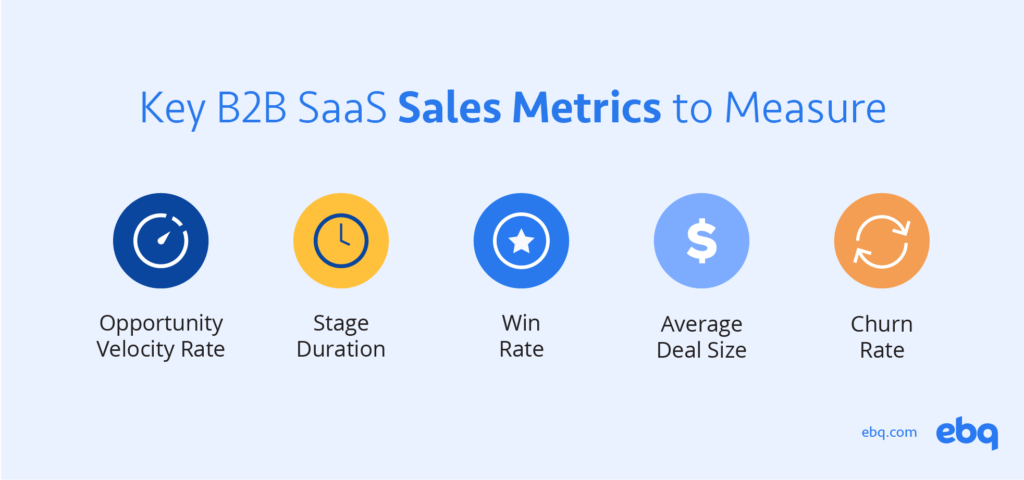
- Opportunity velocity rate: Calculates how fast your prospect moves onto the next stage of your sales pipeline
- Stage duration: Measures how long your prospect stays in every stage of the sales pipeline
- Win rate: Determines the percentage of closed won vs. closed lost deals that closed
- Average deal size Assess how much revenue a deal brings in on average
- Churn rate: Quantifies how many customers stop doing business with your organization over a given period of time
There are many other metrics you can use to assess the effectiveness of your current sales strategy. For example, you can also calculate your average sales cycle length and the number of opportunities in each stage. We’ve covered these metrics within our “Sales Pipeline Metrics to Measure” post.
Factors that impact your sales process
When creating the blueprint of your own software sales process, there are many factors that can change how you implement your procedure:
- Your product/market fit
- Your brand awareness
- Your average sales cycle length
Your first step is to figure out if there’s an existing market for your type of product through the product/market fit analysis.
Product/market fit
When launching your product to a new market, you need to ask yourself:
- Is there an existing demand for your type of solution?
- If so, to what degree does your product satisfy a market demand?
- What is the size of your total addressable market (TAM)?
Keep in mind that if your solution is more of a niche fit, you’ll need to create a strong targeting strategy to go after the right type of customers. In fact, you may need to use an account-based strategy — where you target specific named companies — which will lengthen the sales process.
Brand awareness
Now that you know if people are looking for your type of solution, it’s time to assess how much brand awareness you have in the market today. Especially if you’re creating a groundbreaking solution, you’ll need to drum up demand for your software as a first step.
If you’re noticing that your competitors are currently taking up a lot of space in your market, don’t fret. Instead, look for ways to promote your brand — such as through SDR outreach and a thought leadership marketing strategy.
Without proper branding, you’ll risk lengthening your sales cycle because your SDRs will need to spend more time and effort getting your prospects past the initial lead generation stage. By creating a sense of authority within your space, prospects will see your brand as more trustworthy and keep your organization top-of-mind.
If you’re looking to strengthen your marketing efforts, our marketing specialists can create a wide range of assets to boost your brand awareness. Visit our marketing page to learn more.
Average sales cycle length
Your average sales cycle length will be impacted based on the complexity of your product. However, that’s not the only factor that can lengthen your sales cycle.
Studies have shown that the average sales cycle length for a SaaS organization is 84 days. This number can change depending on your average annual contract value (ACV).


One of the most effective ways to shorten the sales cycle length is implementing the SDR/AE sales model. Unlike traditional sales processes, you’re splitting up the sales cycle between a sales development representative (SDR) and an account executive (AE). That way, you’re making sure you’re introducing as many high-quality prospects as possible to your sales pipeline while taking the time to follow up on hot leads.
Another tip to shorten sales cycles: if your organization is offering free trials, we recommend keeping it to 14 days or less. Think about it: a 30-day free trial will automatically add an additional month to your sales cycle. From our experience, 2 weeks is an adequate amount of time to experiment with your tool without stretching the sales process.
The beauty of any sales process is that you can make the process work for your unique business needs. That means there’s no right or wrong answer! In fact, you should be monitoring your sales process, looking for opportunities for improvement, and evolving the process.
Understanding the B2B SaaS sales stages
Our B2B SaaS sales process is designed to help you maximize your sales pipeline and go after relevant SaaS leads. Because it’s not a “one size fits all” process, we encourage you to personalize the process to fit your business needs.
In this post, we’ve covered:
- The 5 steps of a B2B SaaS sales process
- The unique challenges a B2B SaaS sales team faces
- What factors can impact your sales strategies
If you’re looking to maximize your SaaS sales while keeping your overhead costs low, EBQ’s sales team may be the right fit for you. Our outsourced sales team has the experience and the technology know-how to sell your software effectively. Contact us to learn more.